 Microbiology is a branch of biology that studies microorganisms. [1] The object of study usually is all beings (life) which needs to be seen with a microscope, especially bacteria, fungi, microscopic algae, protozoa, and Archaea. Viruses are often also included even though not fully be regarded as living beings. [2]
Microbiology is a branch of biology that studies microorganisms. [1] The object of study usually is all beings (life) which needs to be seen with a microscope, especially bacteria, fungi, microscopic algae, protozoa, and Archaea. Viruses are often also included even though not fully be regarded as living beings. [2]Microbiology began since the invention of the microscope and became a very important field in biology after Louis Pasteur can explain the process of fermenting grapes (wine) and make rabies serum [2] The rapid development of biology in the 19th century particularly experienced in this field and provides a basis for opening Other important fields: biochemistry.
The application of microbiology at present entered various fields and can not be separated from other branches as required also in the fields of pharmacy, medicine, agriculture, nutrition science, chemical engineering, even up to astrobiology and archeology. [1]Table of contents
[Hide]
* 1 History of Microbiology
o 1.1 Era Robert Hooke and Antoni van Leeuwenhoek
o 1.2 Era Pasteur
o 1.3 Era Robert Koch
o 1.4 Era General Microbiology
+ 1.4.1 Martinus Beijerinck and enrichment culture techniques
+ 1.4.2 Kemolitotrofi Sergei Winogradsky and Concepts
* 2 Modern Microbiology
* 3 The term is used in anti-microorganism
* 4 The mechanism of action of an anti-microorganism
* 5 factors - factors that affect the resistance of microorganisms to the substance - the substance Antimikroorganisme
* 6 References
* 7 See also
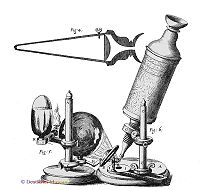
[Edit] History of MicrobiologyIllustration of the microscope used by Robert Hooke in 1664. The objective lens control lever mounted on the end (G), with a focus on the specimen using a single lens (1)[Edit] Era of Robert Hooke and Antoni van Leeuwenhoek
Robert Hooke (1635-1703) is a mathematician, natural historian, and expert microscopy English origin. [2] In his famous book, Micrographia (1665), Hooke illustrates the structure of the fruit of a type of fungus [2] This is the first description of the microorganisms which was published. [2]Antoni van Leewenhoek face immortalized in stamps in the Netherlands in 1937
The first person to see bacteria is the Antoni van Leeuwenhoek (1632-1723), a Dutch amateur microscope maker. [2] In 1684, van Leeuwenhoek microscope uses a very small result of his own work to observe a variety of microorganisms in natural materials. [2] Leeuwenhoek's microscopes used a magnifying glass was then shaped bikonveks with a single specimen is placed between the Apertura small corner on the metal barrier. [3] The device is held close to the eye and the objects on the other side of the lens is adjusted to get the focus [3]. With that tool, Leewenhoek obtain an appropriate contrast between the bacteria floating in the background so it can be seen and distinguished clearly [3]. He found the bacteria in the year 1676 while studying the infusion and water pepper (pepper-water infusion). [2] Van Leeuwenhoek reported his find in a letter to the Royal Society of London, published in English in 1684. [2] Illustration van Leewenhoek about the findings of microorganisms known as the "wee animalcules". [2][Edit] The era of PasteurPasteur's experiments Scheme
In years since, many other observations that confirm the results of van Leeuwenhoek's observations, but the increase of understanding the nature and advantages of microorganisms is running very slow until the next 150 years. [2] Recently in the 19th century, ie after the production of microscopes increases rapidly, then human curiosity microorganisms will begin to grow again. [2] Louis Pasteur is widely known for his theory of spontaneous generation, living organisms derived from living organisms as well. [2] The experiments of Pasteur using a sterilized broth and squash goose neck to prove the existence of microorganisms. [2][Edit] Era of Robert Koch
Since the 16th century, has been known that there is a disease-causing agent that can transmit the disease. [2] After its discovery, it is believed that the microorganism is the agent in question, but yet there is never any evidence. [2] Robert Koch (1842-1910) , a German doctor was the first person who invented the concept of the relationship between infectious diseases and microorganisms by including the experimental evidence. [4] [2] The concept raised by Koch is known as Koch's postulates and is now the gold standard determination of infectious diseases. [2][Edit] Era of General Microbiology
General microbiology refers to non-medical aspects of microbiology. [2] The two giants are known in this era is Beijerinck and Winogradsky. [2] The two began aspects of environmental microbiology [5][Edit] Culture Techniques Martinus Beijerinck and enrichment
Martinus Beijerinck (1851-1931) was a Dutch professor who contributed greatly to the enrichment culture techniques. [2] In this technique, microorganisms isolated from the wild and grown in the laboratory by manipulating nutrients and incubation conditions. [2] Using this technique, Beijerinck succeeded in isolating pure cultures of microorganisms various water and soil for the first time. [2][Edit] Sergei Winogradsky and Concepts Kemolitotrofi
Work Sergei Winogradsky (1856-1953), from Russia, similar to that done Beijerinck, but he is steeped bacteria involved in the cycle of nitrogen and sulfur cycles. [2] The concept of the inception kemolitotrofi relating to the relationship between the oxidation of inorganic compounds with energy conservation. [2] By using enrichment techniques, Winogradsky succeeded mengisioalsi nitrogen fixing bacteria, Clostridium pasteurianum which are anaerobic, and as a forerunner to the concept of nitrogen fixation. [2][Edit] Modern MicrobiologyA worker in the lab are observing the growth of bacteria on a petri dish
Entering the 20th century, began to develop two branches of microbiology are still interconnected: microbiological basis (basic) and applied microbiology (applied). [2] refers to the basic microbiology of new discoveries in this field. [2] While referring applied microbiology on aspects of problem solving (problem solving) are associated with this field. [2] Since the discovery of the concept of DNA was then the field enter the era of molecular microbiology. [2] The success of DNA sequencing uncovered phylogenetic relationships (evolutionary) between different types of bacteria. [ 2][Edit] The term is used in anti-microorganism
Bacteriostatic: The ability to inhibit the proliferation of bacteria temporary. [6] So when the substance is not there, the bacteria can multiply re-
Bactericidal: Chemicals that kill the bacteria permanently. [6] Disinfectants: Material - a chemical used to kill pathogenic microorganisms that exist in inanimate objects. [6]
Sterile: Free from the life of pathogenic microorganisms. [7] Septic: The existence of bacterial pathogens in living tissue in a process of infection. [8][Edit] Mechanism of action of an anti-microorganism
1. Destruction of DNA
2. Denaturation of proteins
3. Disturbances in the group Sulfhidirl
4. Chemical antagonism
5. destruction of the bacterial cell wall
[Edit] Factors - factors that affect the resistance of microorganisms to the substance - the substance Antimikroorganisme

1. Elements - Physical elements, which include:
1. Heat
2. Irradiation by UV rays
3. cooling at a standard temperature
2. Elements - chemical elements, which include:
1. Alcohol
2. Heavy metal ions
3. Detergent
4. Oxidants
Mikrologi Images
No comments:
Post a Comment